Overview
In this tutorial, we will learn how to create a web application using Spring 4 MVC and Hibernate ORM Framework Annotation. We will be writing a simple CRUD Application using Spring 4 MVC and Hibernate 4 with MySQL Database, Eclipse IDE.Follow the steps mentioned below to develop this application.
Watch Tutorial
Setting up Database
Execute the following MySQL script in order to create a database named jack_rutorial_demo with a table named customer.CREATE DATABASE `jack_rutorial_demo`; CREATE TABLE `customer` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `firstname` varchar(45) NOT NULL DEFAULT '', `lastname` varchar(45) NOT NULL DEFAULT '', `gender` varchar(10) NOT NULL DEFAULT '', `address` varchar(200) NOT NULL DEFAULT '', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
Project Structure
The following screenshot shows final structure of the project.Create Maven Project
- Launch Eclipse IDE.
- Go to File-> New-> Others... Select Maven Project under Maven category then click Next.
- In New Maven Project wizard, select "Create a simpel project(skip archetype selection)" and click on Next
- In next wizard, type "com.jackrutorial" in the "Group ID:" field
- Type "SpringMVCHibernateExample" in the "Artifact Id:" field
- Packaging -> War
- Click Finish.
Maven Dependencies
We will update pom.xml file to add the required dependencies for the following dependencies.<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.jackrutorial</groupId>
<artifactId>SpringMVCHibernateExample</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>4.3.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
<version>4.3.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>jstl</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>4.3.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-orm</artifactId>
<version>4.3.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId>
<version>4.3.6.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.validation</groupId>
<artifactId>validation-api</artifactId>
<version>1.1.0.Final</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<pluginManagement>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.4</version>
<configuration>
<warSourceDirectory>src/main/webapp</warSourceDirectory>
<failOnMissingWebXml>false</failOnMissingWebXml>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</pluginManagement>
</build>
</project>
Configure WebApp and Hibernate
To configure WebApp, we create class WebConfig, class WebInitializer in src folder with package name com.jackrutorial.config and write the following code in it.
WebConfig.java
package com.jackrutorial.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ResourceHandlerRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.view.JstlView;
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
@ComponentScan(basePackages = { "com.jackrutorial" })
public class WebConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
registry.addResourceHandler("resources/**").addResourceLocations("/resources/");
}
@Bean
public InternalResourceViewResolver viewResolver(){
InternalResourceViewResolver viewResolver = new InternalResourceViewResolver();
viewResolver.setViewClass(JstlView.class);
viewResolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/jsp/");
viewResolver.setSuffix(".jsp");
return viewResolver;
}
}
WebInitializer.java
package com.jackrutorial.config;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer;
public class WebInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
@Override
protected Class[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return new Class[] { WebConfig.class};
}
@Override
protected Class[] getServletConfigClasses() {
return null;
}
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[] { "/" };
}
}
To configure hibernate, we create class HibernateConfig in src folder with package name com.jackrutorial.config and write the following code in it.
HibernateConfig.java
package com.jackrutorial.config;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource;
import org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.HibernateTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.LocalSessionFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement
@ComponentScan({ "com.jackrutorial.config" })
@PropertySource(value = { "classpath:config.properties" })
public class HibernateConfig {
@Autowired
private Environment environment;
@Bean
public LocalSessionFactoryBean sessionFactory() {
LocalSessionFactoryBean sessionFactory = new LocalSessionFactoryBean();
sessionFactory.setDataSource(dataSource());
sessionFactory.setPackagesToScan(new String[] { "com.jackrutorial.model" });
sessionFactory.setHibernateProperties(hibernateProperties());
return sessionFactory;
}
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
DriverManagerDataSource dataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName(environment.getRequiredProperty("jdbc.driverClassName"));
dataSource.setUrl(environment.getRequiredProperty("jdbc.url"));
dataSource.setUsername(environment.getRequiredProperty("jdbc.username"));
dataSource.setPassword(environment.getRequiredProperty("jdbc.password"));
return dataSource;
}
private Properties hibernateProperties() {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.put("hibernate.dialect", environment.getRequiredProperty("hibernate.dialect"));
properties.put("hibernate.show_sql", environment.getRequiredProperty("hibernate.show_sql"));
properties.put("hibernate.format_sql", environment.getRequiredProperty("hibernate.format_sql"));
return properties;
}
@Bean
@Autowired
public HibernateTransactionManager transactionManager(SessionFactory s) {
HibernateTransactionManager txManager = new HibernateTransactionManager();
txManager.setSessionFactory(s);
return txManager;
}
}
We still have to configure config.properties file in classpath. We create a config.properties file in src/main/resources folder and write the following code in it.
jdbc.driverClassName = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jdbc.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jack_rutorial_demo jdbc.username = root jdbc.password = root hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect hibernate.show_sql = true hibernate.format_sql = false
MySQL Database Name: jack_rutorial_demo
Password for MySQL: root
Username for MySQL: root
Create Hibernate Entity Bean
Create a Customer class under com.jackrutorial.model package and write the following code in it.Customer.java
package com.jackrutorial.model;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name="customer")
public class Customer {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private int id;
@Column(name = "firstname")
private String firstname;
@Column(name = "lastname")
private String lastname;
@Column(name = "gender")
private String gender;
@Column(name = "address")
private String address;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getFirstname() {
return firstname;
}
public void setFirstname(String firstname) {
this.firstname = firstname;
}
public String getLastname() {
return lastname;
}
public void setLastname(String lastname) {
this.lastname = lastname;
}
public String getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(String gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
In the above code, we are using JPA annotations in our entity bean class. Our entity bean maps to customer table in MySQL database.
Creating DAO Layer
Create a CustomerDao Interface under com.jackrutorial.dao package and write the following code in it.CustomerDao.java
package com.jackrutorial.dao;
import java.util.List;
import com.jackrutorial.model.Customer;
public interface CustomerDao {
public List listAllCustomers();
public void saveOrUpdate(Customer customer);
public Customer findCustomerById(int id);
public void deleteCustomer(int id);
}
Create a CustomerDaoImpl class implements CustomerDao Interface under com.jackrutorial.dao package and write the following code in it.
CustomerDaoImpl.java
package com.jackrutorial.dao;
import java.util.List;
import org.hibernate.Criteria;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.jackrutorial.model.Customer;
@Repository
public class CustomerDaoImpl implements CustomerDao {
@Autowired
private SessionFactory sessionFactory;
protected Session getSession(){
return sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public List listAllCustomers() {
Criteria criteria = getSession().createCriteria(Customer.class);
return (List) criteria.list();
}
public void saveOrUpdate(Customer customer) {
getSession().saveOrUpdate(customer);
}
public Customer findCustomerById(int id) {
Customer customer = (Customer) getSession().get(Customer.class, id);
return customer;
}
public void deleteCustomer(int id) {
Customer customer = (Customer) getSession().get(Customer.class, id);
getSession().delete(customer);
}
}
Creating Service Layer
Create a CustomerService Interface under package com.jackrutorial.service package and write the following code in it.CustomerService.java
package com.jackrutorial.service;
import java.util.List;
import com.jackrutorial.model.Customer;
public interface CustomerService {
public List listAllCustomers();
public void saveOrUpdate(Customer customer);
public Customer findCustomerById(int id);
public void deleteCustomer(int id);
}
Create a CustomerServiceImpl class implements CustomerService Interface under com.jackrutorial.service package and write the following code in it.
CustomerServiceImpl.java
package com.jackrutorial.service;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import com.jackrutorial.dao.CustomerDao;
import com.jackrutorial.model.Customer;
@Service
@Transactional
public class CustomerServiceImpl implements CustomerService {
CustomerDao customerDao;
@Autowired
public void setCustomerDao(CustomerDao customerDao) {
this.customerDao = customerDao;
}
public List listAllCustomers() {
return customerDao.listAllCustomers();
}
public void saveOrUpdate(Customer customer) {
customerDao.saveOrUpdate(customer);
}
public Customer findCustomerById(int id) {
return customerDao.findCustomerById(id);
}
public void deleteCustomer(int id) {
customerDao.deleteCustomer(id);
}
}
Creating Controller Layer
Create a CustomerController class under package com.jackrutorial.controller package and write the following code in it.CustomerController.java
package com.jackrutorial.controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import com.jackrutorial.model.Customer;
import com.jackrutorial.service.CustomerService;
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value="/customer")
public class CustomerController {
@Autowired
CustomerService customerService;
@RequestMapping(value="/list", method=RequestMethod.GET)
public ModelAndView list(){
ModelAndView model = new ModelAndView("customer/list");
List list = customerService.listAllCustomers();
model.addObject("list", list);
return model;
}
@RequestMapping(value="/update/{id}", method=RequestMethod.GET)
public ModelAndView update(@PathVariable("id") int id){
ModelAndView model = new ModelAndView("customer/form");
Customer customer = customerService.findCustomerById(id);
model.addObject("customerForm", customer);
return model;
}
@RequestMapping(value="/delete/{id}", method=RequestMethod.GET)
public ModelAndView delete(@PathVariable("id") int id){
customerService.deleteCustomer(id);
return new ModelAndView("redirect:/customer/list");
}
@RequestMapping(value="/add", method=RequestMethod.GET)
public ModelAndView add(){
ModelAndView model = new ModelAndView("customer/form");
Customer customer = new Customer();
model.addObject("customerForm", customer);
return model;
}
@RequestMapping(value="/save", method=RequestMethod.POST)
public ModelAndView save(@ModelAttribute("customerForm") Customer customer){
customerService.saveOrUpdate(customer);
return new ModelAndView("redirect:/customer/list");
}
}
Creating JSP Views
Create customer folder under src\main\webapp\WEB-INF\jsp\customer folder.Create list.jsp file under src\main\webapp\WEB-INF\jsp\customer folder and write the following code in it.
list.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"
pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %>
<%@ taglib uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags" prefix="spring" %>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1">
<title>Customer</title>
</head>
<body>
<spring:url value="/customer/add" var="addURL" />
<a href="${addURL }">Add new Customer</a>
<table width="100%" border="1">
<tr>
<td>ID</td>
<td>Firstname</td>
<td>Lastname</td>
<td>Gender</td>
<td>Address</td>
<td colspan="2">Action</td>
</tr>
<c:forEach items="${list }" var="customer" >
<tr>
<td>${customer.id }</td>
<td>${customer.firstname }</td>
<td>${customer.lastname }</td>
<td>${customer.gender }</td>
<td>${customer.address }</td>
<td>
<spring:url value="/customer/update/${customer.id }" var="updateURL" />
<a href="${updateURL }">Update</a>
</td>
<td>
<spring:url value="/customer/delete/${customer.id }" var="deleteURL" />
<a href="${deleteURL }">Delete</a>
</td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>
</table>
</body>
</html>
Create form.jsp file under src\main\webapp\WEB-INF\jsp\customer folder and write the following code in it.
form.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"
pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%>
<%@ taglib uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags" prefix="spring" %>
<%@ taglib uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" prefix="form" %>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1">
<title>Form</title>
</head>
<body>
<spring:url value="/customer/save" var="saveURL" />
<form:form action="${saveURL }" method="POST" modelAttribute="customerForm">
<form:hidden path="id"/>
<table>
<tr>
<td>Firstname</td>
<td><form:input path="firstname"/></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Lastname</td>
<td><form:input path="lastname"/></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Gender: </td>
<td>
<form:radiobutton path="gender" value="Male" /> Male
<form:radiobutton path="gender" value="Female" /> Female
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Address</td>
<td><form:textarea path="address" rows="3" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td><button type="submit">Save</button></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form:form>
</body>
</html>
Building
- Right click this project
- Select Run As -> Maven clean
- Right click this project
- Select Run As -> Maven install
Configuring Apache Tomcat
- Under Servers tab, click link "No servers are available. Click this link to create a new server ...", select Apache tomcat 7
- Click Finish
- Right click "Tomcat v7.0 Server at localhost [Stopped, Republish]", select "Add and Remove ..."
- Add SpringMVCHibernateExample project, then Click Finish
- Open server.xml file under Servers Folder
- Find line
<Context docBase="SpringMVCHibernateExample" path="/SpringMVCHibernateExample" reloadable="true" source="org.eclipse.jst.jee.server:SpringMVCHibernateExample" />
Update its as below:
<Context docBase="<Project Folder Location>\SpringMVCHibernateExample\target\SpringMVCHibernateExample-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT\" path="/SpringMVCHibernateExample" reloadable="true" />
Watch video add Apache Tomcat Server in Eclipse IDE
Run application & Check result
- Start Apache Tomcat from Eclipse IDE.
- Type the following URLs in browser's address bar to open the customer list.
http://localhost:8080/SpringMVCHibernateExample/customer/list
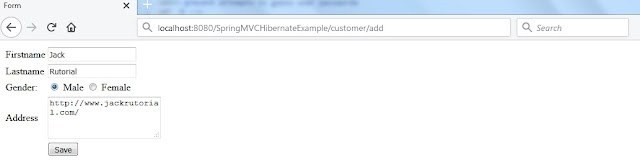
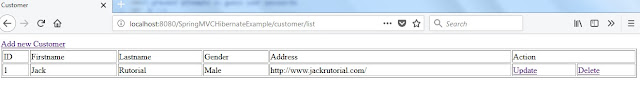
Below screenshots shows the view pages for our application.